Semantic Artefact details
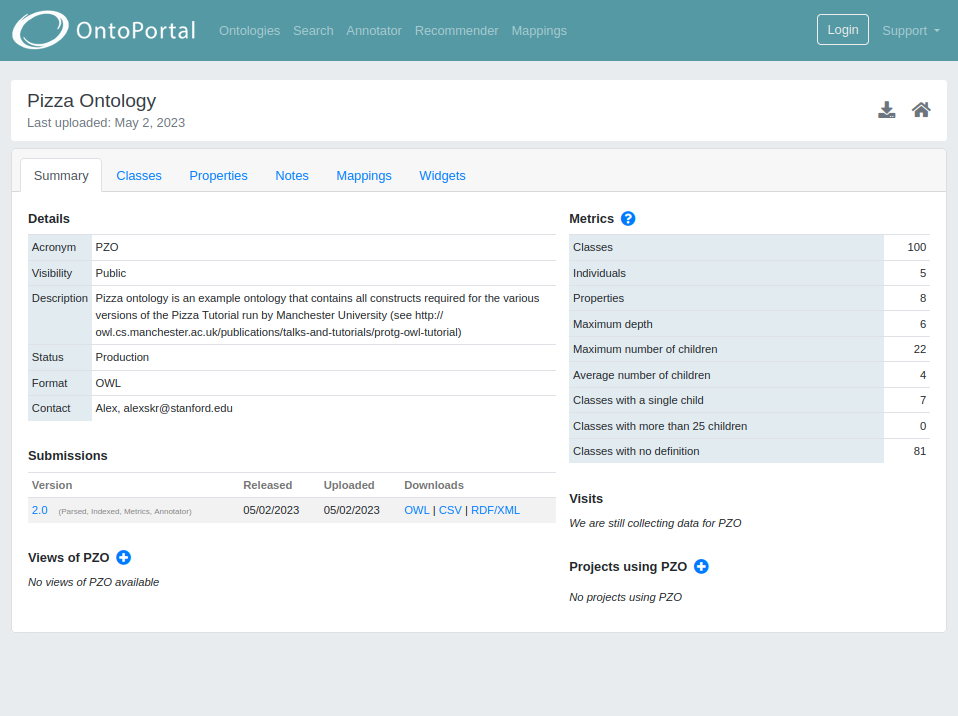
Once the selected ontology has been opened, the summary page shows the different sections. On the left are displayed:
- A menu with different tabs
- Metadata (divided in Details and Additional Metadata)
- Submissions
- Views of the ontology
Metadata Summary
Summary
In the detail area of the summary page, on the left it is displayed the OntoPortal metadata schema for the selected ontology.
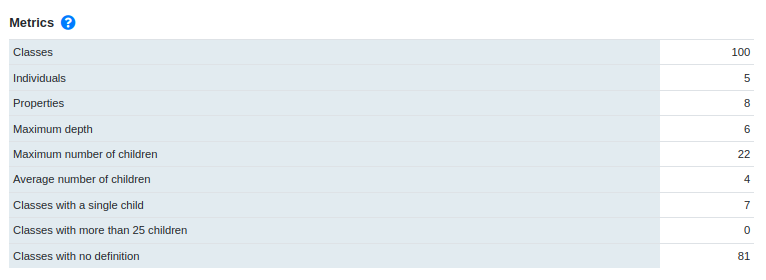
Metrics
This section describes the metrics that OntoPortal computes for each semantic artefact (Figure 7). Metrics start to be computed when a semantic artefact is uploaded and they are part of OntoPortal Metadata Schema.
There are two groups of metrics:
- statistical metrics;
- quality-control and quality-assurance metrics.
Note: some metrics are meaningful only for ontology in a specific representation language (e.g., there are no individuals to count in the ontologies in OBO format).
The Statistical Metrics include:
- Number Of Classes: the number of named (not anonymous) classes in the semantic artefact
- Number Of Individuals: the number of individuals in the semantic artefact
- Number Of Properties: the number of properties or slots in the semantic artefact
- Maximum Depth: the maximum depth of the hierarchy tree:
- for OWL, RDFS, Protege, and UMLS RFF ontologies, only the “is-a” relationship is considered a hierarchical relationship
- for OBO ontologies, the following relationships are considered as hierarchical relationships: “is-a”, “has-part”, “inverse” and “develops-from”
- Maximum Number Of Children: the maximum number of children in the semantic artefact
- Average Number Of Children: the average number of children at one level in the tree
Quality-Control and Quality-Assurance Metrics provide some indication of the quality of the ontology and help ontology authors to improve their quality. The maximum value allowed for all metrics is currently set to 200. Ontologies with more than 200 classes in a category will still have the total number of classes in that category counted, but no list will be available. Please notice that:
- Classes With A Single Child: a list of classes with only one subclass in the hierarchy. While technically there is no problem in having only one subclass, this situation often indicates that either the hierarchy is under-specified, or that the distinction between the class and the subclass is not appropriate;
- Classes With More Than 25 Children: a list of classes that have more than 25 direct subclasses. A class that has more than 25 subclasses could benefit of additional distinctions and categorization;
- Classes With No Definition: a list of classes that have no value for the definition property. For ontologies in OBO and RDRF formats, the property for definition is part of the language. For OWL ontologies, the authors specify this property as part of the ontology metadata (the default is “skos:definition”).
For more details about the metrics generation, please read this. OntoPortal users will be able to access ontology metrics in two ways:
- through the OntoPortal user interface, in the metrics area of the summary page (see example here);
- through a dedicated REST service that returns a JSON (see example below).
The following REST service can be used: https:///ontologies/OntologyAcronym/metrics?apikey=YourAPIKey The service returns a JSON that contains the version id for the ontology and the values for the metrics.
If a given semantic artefact has more than 200 classes identified for a metric, then that metric will provide an error message within the class list. Two messages can appear:
- limitpassed: it means that the 200-class limit was reached. When this error appears, it is followed by the total number of classes in the semantic artefact that matches this metric;
- alltriggered: it means that every class in the semantic artefact matched this metric.
Submissions
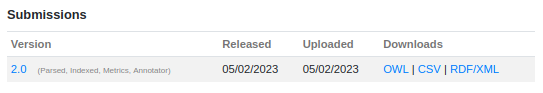
In the submission area, all submissions made for that ontology are available. The table includes four columns:
- Version: shows the different versions loaded into OntoPortal with the status next to it. The labels assigned automatically by the portal are: Parsed (the resource has been parsed), Indexed (the resource has been indexed), Metrics (the metrics for that resource have been calculated) and Annotator (the resource is ready to annotate some text via API or the Annotator tools). OntoPortal indexes the latest submission. The previous submissions will appear with the “Archived” label, which means that submission will no longer be published;
- Released: shows the original release date (mm/dd/yy) of the resource (manually set by the user);
- Uploaded: shows the initial publication date (mm/dd/yy) of the resource in OntoPortal (automatically assigned by the system);
- Downloads: allows the download of the resource in different formats SKOS, OBO, UMLS, OWL, CSV, RDF/XML, depending on the representation language of the resource. Furthermore, when more submissions occur for the same resource, the system performs an automatic download report (Diff) of the differences between the submitted versions.
Views
This area displays the ontology views and allows the creation of new ones. A view is a manageable portion of a larger ontology that is tailored for specific applications and users. When creating a view, the system:
- allows the precise extraction of subsets from a larger resource;
- allows to personalise and use portion of a resource;
- facilitates interoperability between subsets of large ontologies and specific applications. Each displayed view is linked for an easy consultation.
Projects
In this section, you’ll find showcased projects utilising the chosen ontology, with convenient links for easy reference. Logged in users can create new projects. These projects serve as a guide for users to explore ontologies associated with specific projects, offering insights into the contextual usage of these ontologies. Each project page includes a concise project description and a link to the project’s homepage.
Menu
The menu area enables you to explore classes, properties, notes, mappings, and available widgets through tabs. When the chosen resource is a thesaurus, three distinct tabs emerge: the “Classes” tab is substituted with “Concepts,” “Schemes,” and “Collections”.
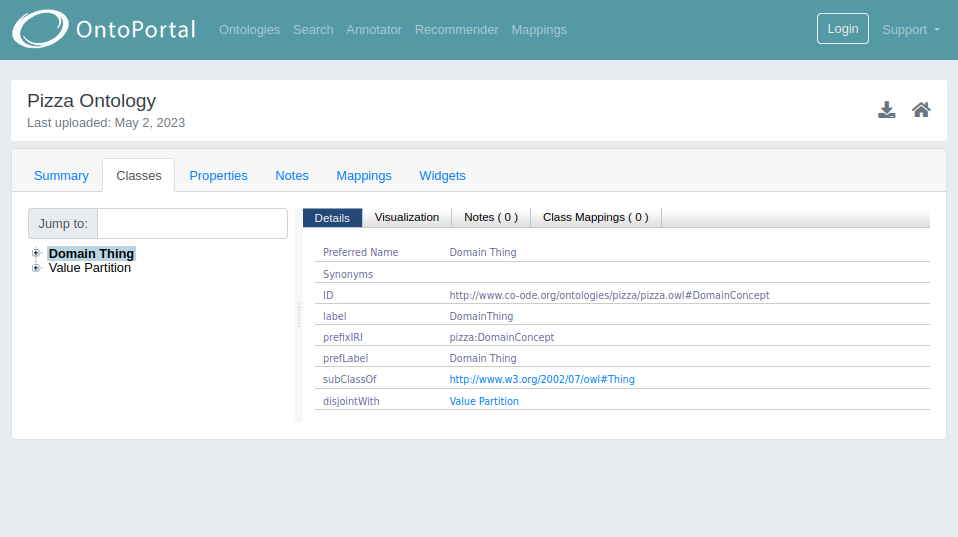
Classes
On the summary page of the ontology, by clicking on tab “Classes”, it is shown:
- on the left side, different views of the resource. If it is an ontology, you will see the “Hierarchical view”, in which classes are organised in a tree-like structure, and the “Date view”, which displays classes based on their creation and modification dates (if these were defined). In the case of a thesaurus the “Collection view” will also be available. In addition, close to the search bar, there is a filter to select different schemes eventually available within a thesaurus;
- on the right side, an area containing Details, Visualization, Notes and Mappings related to the selected class or concept:
- Details: tab showing properties and relationships associated with the selected class/concept.
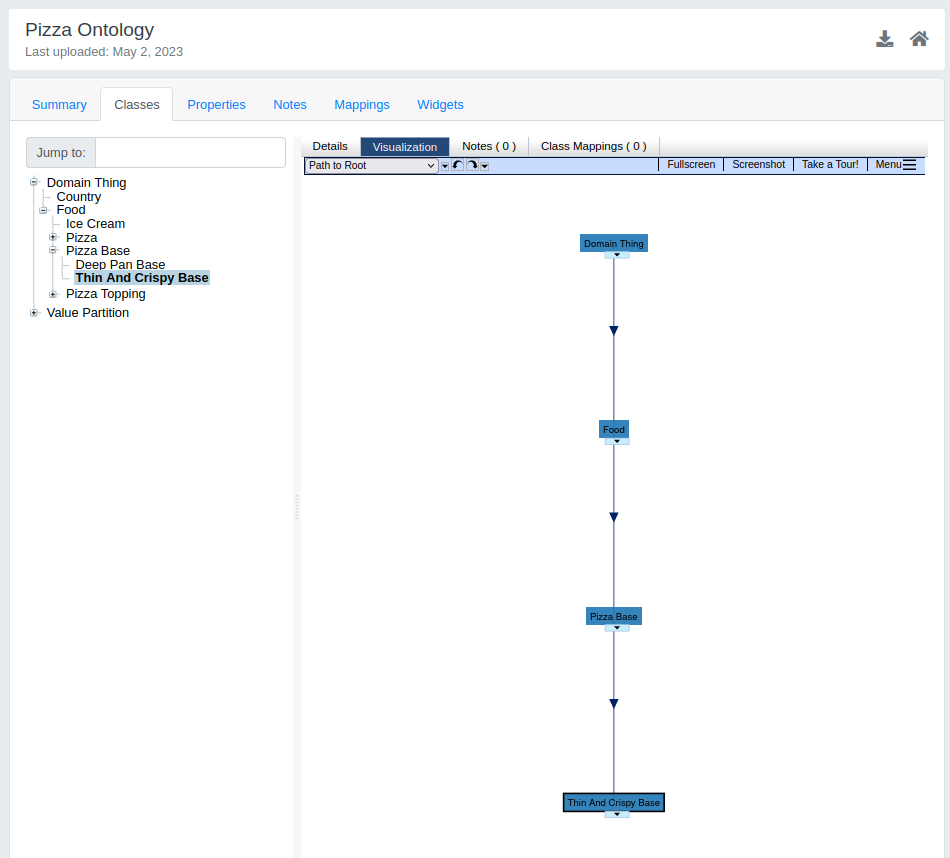
- Visualization: OntoPortal presents ontologies in a graph format, with resource concepts represented as nodes and the relationships between them as edges. By default, the most basic directional relationships (parent/child relationships) are identified by a solid navy-blue line with an arrow pointing to the child concept/class. Mappings are represented by solid light-grey lines.
- Notes: it displays all notes issued by OntoPortal users in relation to the selected class/concept. To issue generic comments or proposals regarding new classes, new relationships, or change properties, users must be logged in.
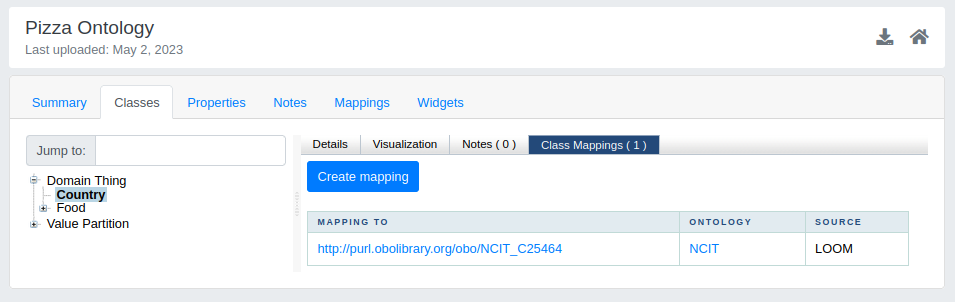
- Class Mappings: tab showing all the mappings associated with the selected class. For each mapping you can see:
- MAPPING TO: the name of the selected class/concept mapped to the class/concept of another resource;
- ONTOLOGY: the ontology of the mapped class/concept;
- RELATIONS: the type of relation that the algorithms have used;
- SOURCE: the mapping algorithm;
- TYPE: the mappings can be internal to the portal or external to the portal;
- ACTIONS: the mappings can be edited or deleted by the administrator of the resource. Logged in users can click on the “Create new Mapping” button to manually insert mappings by filling in the following fields: target ontology or view; target class; details; comment; mapping relation type.
Properties
In the summary page of the chosen ontology, by clicking on the Properties tab all the properties used within the selected ontology are displayed. Similar to the Classes tab, the interactive property tree is shown on the left, while the property details are shown on the right. 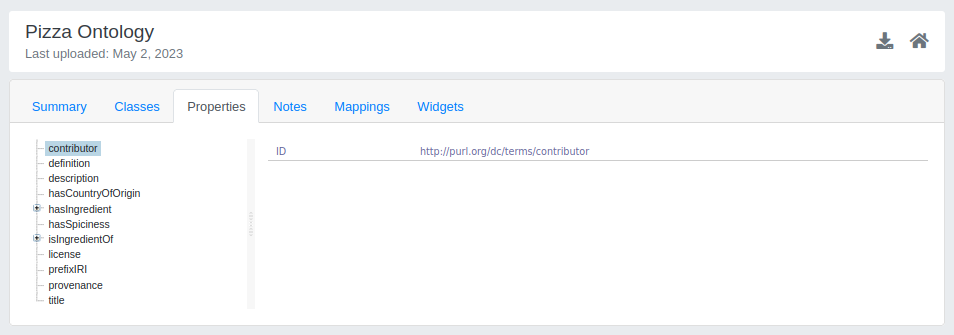
Notes
In the Notes tab users can see all the comments or proposals issued by other registered OntoPortal users. 
- Add a comment: logged in users can send a comment to the owner of the resource by specifying the subject and writing a free text comment.
- Add a proposal: logged in users can send a proposal to the owner of the resource to modify or create new relationships or classes/concepts.
- Subscribe/Unsubscribe to notes emails: users can subscribe to receive emails whenever comments or proposals from other users are provided. Users can manage their subscriptions on the “Account Settings” page and click on the “Unsubscribe” link to stop receiving emails.
Mappings
In the Mappings tab all the mappings of the selected ontology are displayed. The table includes two columns: ontology and Mappings. The first column identifies the ontology to which the selected resource is mapped, and the second column shows the number of mappings. By clicking on a ontology all the mappings are shown. 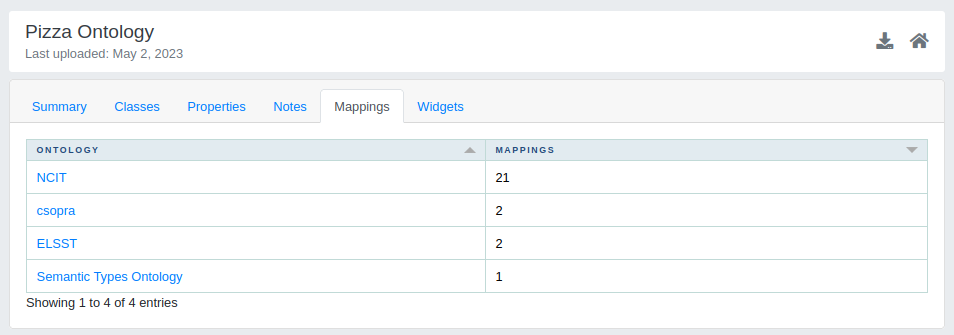
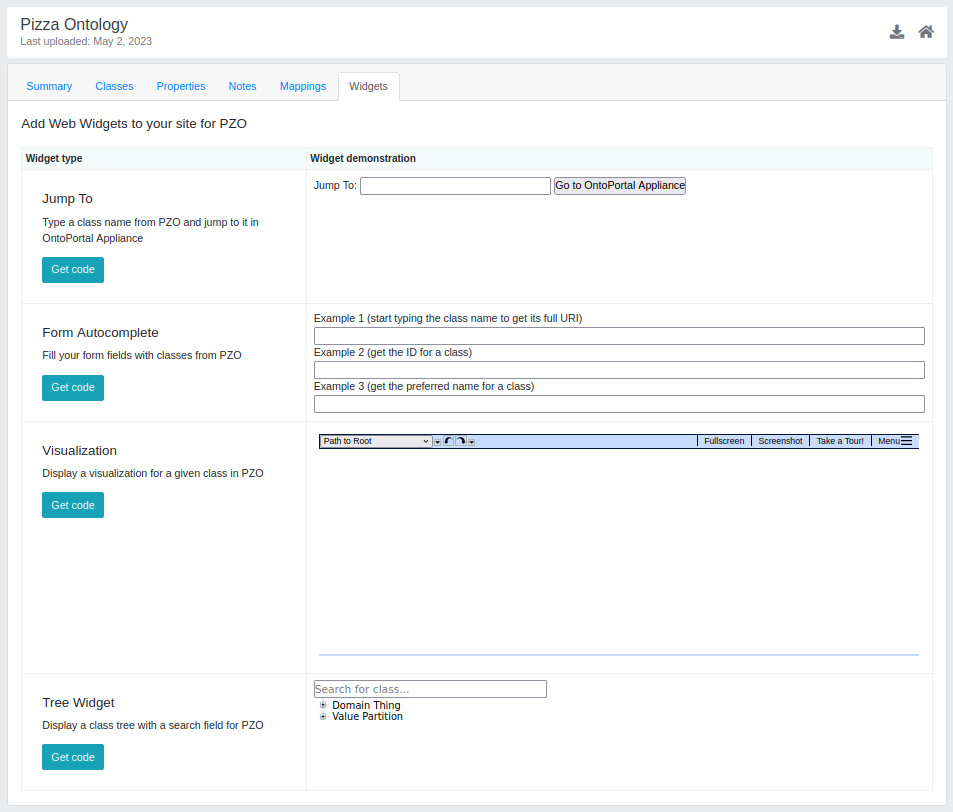
Widgets
Widgets tab contains the different types of widgets that can be incorporated in a web page (Figure 19). The page is divided in two sides, “Widget type” with the “Get code” buttons which lead to short instructions and to the download link of the code to be incorporated, on the right, their relative demos. The types of widgets available in OntoPortal are:
- Jump To: type a class in the selected ontology and jump to it in OntoPortal;
- Form Autocomplete: fill in a field in your form with a class from the selected ontology;
- Visualization: display a visualisation for a given class/concept in the selected ontology;
- Tree Widget: display a tree for classes in the selected ontology with a search field.